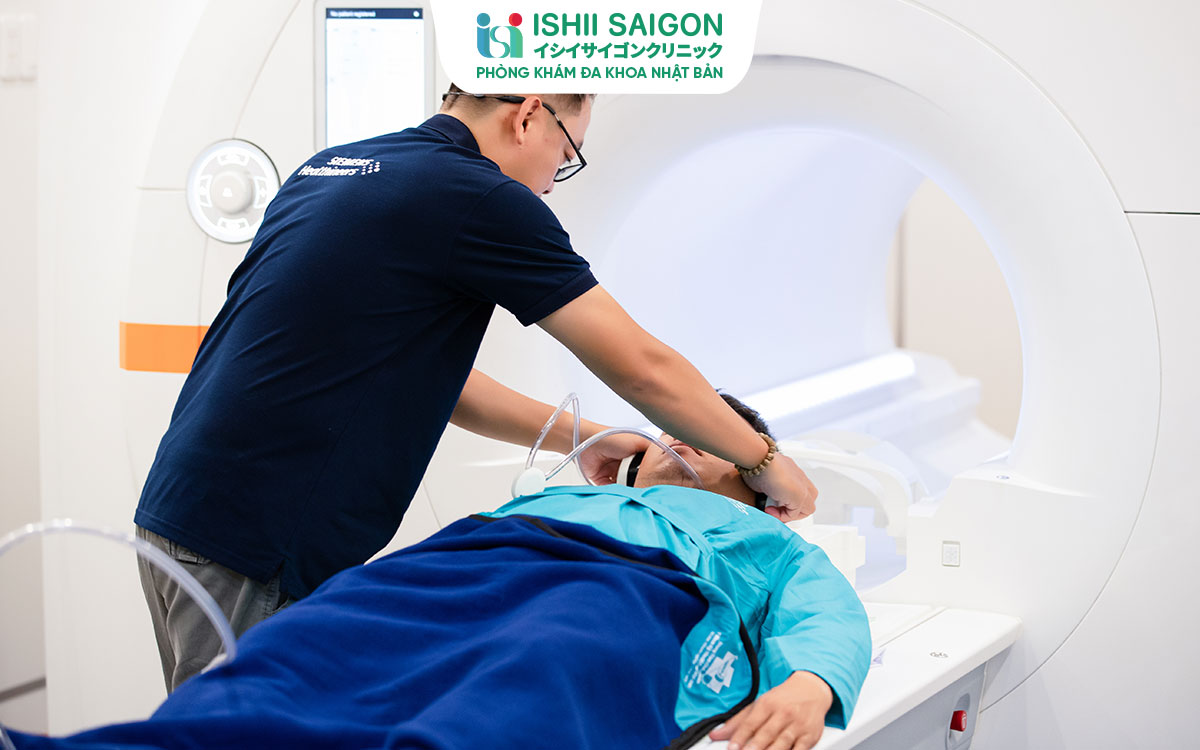
1. Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an advanced diagnostic imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s organs and soft tissues without the need for invasive procedures. MRI is widely applied in healthcare to diagnose and monitor various conditions, particularly brain, spinal cord, muscle, joint disorders, and tumors. Thanks to its non-use of ionizing radiation, unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI is considered a safe and effective method for assessing patient health.
Principle of Operation of MRI Machines
MRI machines operate based on the principles of strong magnetic fields and radio waves interacting with atoms in the body, primarily hydrogen atoms in water. When the body is exposed to a strong magnetic field, the protons in cells align in a specific direction. Then, when the machine emits radio waves into the body, these protons are stimulated and emit return signals. These signals are recorded and processed by the machine to produce high-resolution images of the body’s organs and tissues.
Thanks to this advanced technology, MRI can provide detailed, high-resolution images of soft tissues, enabling doctors to easily detect and accurately diagnose medical conditions.
Key Benefits of MRI in Diagnosis
MRI offers numerous outstanding benefits in diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions, including:
Non-invasive and safe: MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it harmless to the human body compared to other imaging methods like X-rays or CT scans.
Clear Imaging: MRI provides detailed, high-resolution images, enabling doctors to detect abnormalities in the body that are difficult to see with the naked eye.
Ability to Diagnose Various Conditions: MRI is highly effective in detecting conditions related to the brain, spinal cord, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs such as the liver and kidneys.
Early Detection of Conditions: With its ability to provide detailed images of tissue structures, MRI enables early detection of conditions, especially cancer, increasing the chances of effective treatment.
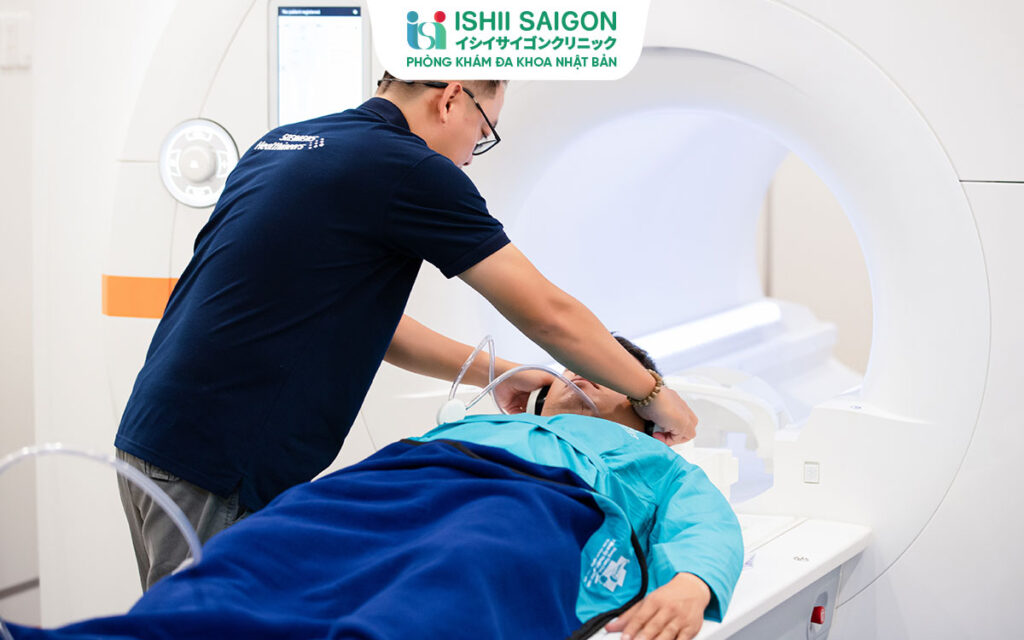
2. Diagnosing Neurological Disorders with MRI
One of the important applications of MRI is in diagnosing neurological disorders. By producing clear images of the brain and spinal cord, MRI helps detect abnormalities such as:
Brain tumors: MRI can detect the presence of brain tumors, determine their size, location, and extent of spread.
Stroke: MRI can help identify areas of damage caused by a stroke and monitor the patient’s recovery progress.
Spinal cord disorders: Conditions such as herniated discs, myelitis, or spinal cord injuries can be detected through MRI.
Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases: MRI helps detect structural changes in the brain, supporting the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
3. MRI in Tumor Detection
MRI is an ideal method for detecting and monitoring tumor-related conditions, including both benign and malignant tumors. This technique is highly useful for determining the size, location, and extent of tumor spread. MRI is particularly effective in detecting types of tumors such as:
Breast tumors: MRI can detect tumors in breast tissue, especially in high-risk patients.
Liver and kidney tumors: MRI helps detect tumors in the liver and kidneys that other diagnostic methods might overlook.
Brain tumors: MRI provides detailed images of brain tumors, helping assess their severity and plan appropriate treatment.
Learn more: MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) at Ishii Saigon Japanese General Clinic
4. MRI Applications in Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis
MRI also plays a crucial role in diagnosing cardiovascular diseases. Cardiac MRI helps assess the condition of the heart muscle, blood vessels, and heart structure without the need for surgery. Some common applications of MRI in cardiology include:
Heart function assessment: MRI can help evaluate heart function, determine the heart's pumping ability, and detect issues such as heart failure.
Coronary artery disease: MRI helps detect blockages or narrowing of the coronary arteries, which can lead to a heart attack.
Myocarditis: MRI can detect signs of inflammation in the heart muscle, aiding in the diagnosis of this condition.
5. Limitations and Challenges in MRI Use
Although MRI has many advantages, there are also some limitations and challenges in its use:
High cost: MRI scans are often more expensive compared to other diagnostic methods such as X-rays or ultrasound.
Long scan time: The MRI process can take between 30 to 60 minutes, which may be uncomfortable for some patients.
Not suitable for some patients: MRI is not suitable for patients with metal implants in their body (such as pacemakers or artificial heart valves), as the strong magnetic field can damage the device or pose a risk to the patient.
Difficulty in imaging children: The requirement for patients to remain still for an extended period can be challenging for children or patients with mobility issues.
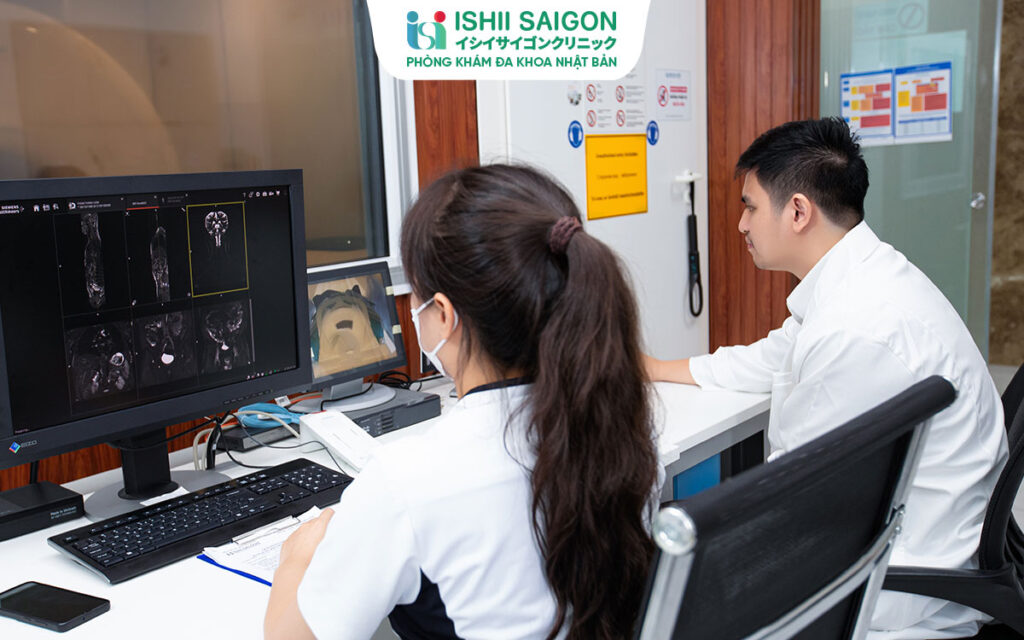
6. 3.0 Tesla MRI at Ishii Sài Gòn
At Ishii Sài Gòn Japanese General Clinic, the 3.0 Tesla MRI is used to provide the sharpest and most detailed images. With the advanced 3.0 Tesla MRI machine, Ishii Sài Gòn is committed to delivering accurate and fast results for patients. In particular, the 3.0 Tesla MRI significantly improves image quality, helping doctors detect diseases at an early stage and offering more effective treatment options.
With a team of highly specialized doctors and modern facilities, Ishii Sài Gòn Clinic is always a trusted choice for patients who need MRI scans to diagnose serious conditions.
With its outstanding benefits in diagnosing and detecting conditions, MRI is an indispensable method in modern medicine. If you need to diagnose a condition or monitor your health, don't hesitate to visit Ishii Sài Gòn for consultation and undergo an MRI scan with the advanced 3.0 Tesla technology.






